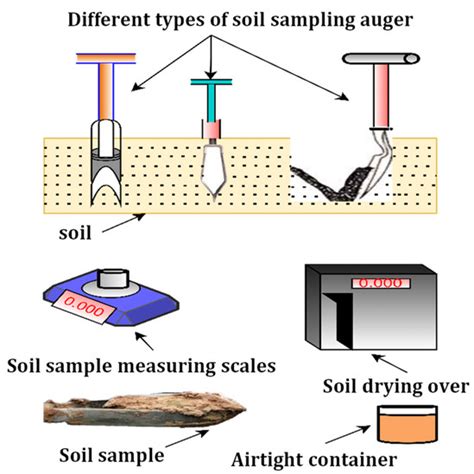
gravimetric method in soil moisture|soil moisture content chart : commercial Also known as the drying method, the gravimetric method determines the moisture content of soil using a sample that is weighed prior to and after being dried. The moisture content can then be defined by establishing the weight . É uma funcionalidade desenvolvida para verificar a proximidade entre um anunciante e um visitante. Assim, um visitante poderá visualizar os perfis de anunciantes que estiverem .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 8 de dez. de 2022 · 测速网(SpeedTest.cn)为您提供在线免费网速测试,Ping测试,路由测试优质服务,拥有海内外,网通、联通、电信、移动、长城宽带、鹏博士等多个全面速度测试点,欢迎您的使用。
soil moisture measurement methods pdf
custom how to read digital soil moisture meter rapitest
Principle. The gravimetric method allows the quantification of the soil moisture content based on the loss of weight (mass) due to the loss of water by heating the soil to a temperature of .Measurement of soil moisture content by gravimetric method. The soil moisture content may be expressed by weight as the ratio of the mass of water present to the dry to the dry weight of .Also known as the drying method, the gravimetric method determines the moisture content of soil using a sample that is weighed prior to and after being dried. The moisture content can then be defined by establishing the weight .The weight method provides a direct measurement of soil water mass content, which can be used to adequately calculate irrigation requirements, assess soil moisture conditions for crop .
The objectives of this chapter are to: (a) gain basic knowledge about soil moisture and its importance; (b) understand different methods and principles of measurement of soil .
With this in view, efforts have been made in this paper to critically evaluate all the soil moisture measurement techniques, limitations associated with them and the influence of .This procedure outlines the process for the determination of cation exchange capacity (CEC) and exchangeable bases (calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium) in soil using 1N .Summary. The gravimetric method is technically unsophisticated and requires only simple equipment, much of which is usually available in laboratories. The method may be divided into . The analysis was carried out by the gravimetric method. The gravimetric method is a conventional method but the most widely used to predict soil moisture [8].How it works: 1) weigh the of aluminum .
A comparison of soil sensing methods. Gravimetric water content is a good first principles measurement but is time consuming, destructive, and only gives a snapshot in time. Soil water content sensors provide a time series, enable .
The gravimetric method allows the quantification of the soil moisture content based on the loss of weight (mass) due to the loss of water by heating the soil to a temperature of 105 °C ± 5 °C until constant mass is achieved. Soil moisture is expressed as a percentage of the mass of water in a given soil mass (e.g. grams of water The amount of surface soil moisture (SSM) is a crucial ecohydrological natural resource that regulates important land surface processes. It affects critical land–atmospheric phenomena, including the division of energy and water (infiltration, runoff, and evaporation), that impacts the effectiveness of agricultural output (sensible and latent heat fluxes and surface air .Soil water content affects the moisture and amount of nutrients available to plants and soil aeration status. Soil water content can be measured on a mass or volume basis. Gravimetric soil water content is the mass of water in the soil, measured as the difference between the moist soil and the soil dried at 105°C, known as the oven-dry weight.
soil moisture content chart
Gravimetric water content is a good first principles measurement but is time consuming, destructive, and only gives a snapshot in time. Soil water content sensors provide a time series, enable profile sensing over time, and avoid destructive sampling, though a sensor is still inserted into the soil.Remote sensing provides a time series at a limited scale but is extremely powerful . Soil Drying Method (select method most appropriate): 1) 250 Watt infrared heating lamp, 1 or 2 bulbs, that reach temperatures of 65 – 90 oC for 2-3 . GLOBE® 2014 Gravimetric Soil Moisture Protocols - 4 Soil (Pedosphere) soil mass to get a normalized value for soil water content. This normalized value can Abstract Based on the gravimetric-technique-measured soil relative wetness and the observed soil characteristic parameters from 1992 to 2013 in China, this study derives a user-convenient monthly volumetric soil moisture (SM) dataset from 732 stations for five soil layers (10, 20, 50, 70, and 100 cm). The temporal–spatial variations in SM and its relationship with .Another way of communicating soil water content is on a mass or volume basis. Direct measurements include gravimetric (θg) and volumetric water content (θv). The gravimetric method measures the mass of water in a given mass of oven-dry soil (g g-1).The mass of water is the difference in weight between the soil sample before and after drying it in an oven.
In this paper, an attempt has been made to evaluate different soil moisture estimation methods right from conventional methods like gravimetric soil moisture techniques to most advanced tools like .
Gravimetric Soil Moisture Testing and Detection. Gravimetric soil moisture detection is a method that uses evaporation, flushing, and a chemical reaction to extract water from a soil sample and calculate soil moisture based . The amount of moisture present in the soil can be expressed in percentage either as gravimetric soil moisture content, . sensor technique consists of two probes viz. heater and temperature sensor probes for measuring soil volumetric moisture content. The method is based on the application of an instantaneous pulse of heat to an infinite line .
Ground-based methods. In principle, ground-based methods is one of spatial (area where process occurs) data acquisition vary from field observation, in situ measurement, and land survey (Bakker et al. 2004).Spatial variability determination of soil water content is important in scientific issues and applications (Jonard et al. 2019).Moisture measurement techniques are . Based on the gravimetric-technique-measured soil relative wetness and the observed soil characteristic parameters from 1992 to 2013 in China, this study derives a user-convenient monthly . The gravimetric process is widely accepted as the most accurate process for establishing the true moisture content of a material sample and determining its moisture composition as described in BRE .The subject of soil moisture is also of great importance to the hydrologist, forester, and soils engineer. Much equipment and many methods have been developed to measure soil moisture under field conditions. . The gravimetric method is concluded to be the most satisfactory method for most problems requiring onetime moisture-content data. The .
Methodological problems discussed include the site destruction caused by the gravimetric method and the fact that the method itself accounts for some of the variability found in soil moisture distribution, and possibly for supposedly significant changes in soil moisture content in time and space. With the gravimetric method, soil moisture is determined by taking a soil sample from the desired soil depth, weighing it, drying it in an oven (for 24 hours at 220 degrees F), and then reweighing the dry sample to determine how much water was lost. This method is simple and reliable. Unfortunately, it is not practical for scheduling irrigation .
where \(\theta\) is the gravimetric soil water content (%), S is the soil suction (bar), and A is the SWHC.. Employing the equation above, we measured soil water content at a potential of − 20 . Terms such as methods of soil moisture estimation, UNCCD, payment for ecosystem services, gravimetric methods, use of neutron probe, time domain reflectometry, tensiometers, remote sensing for soil moisture estimation, capacitive sensor, gypsum blocks for soil moisture, pressure plate apparatus, and ground penetrating radar were sought in the .Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass. The principle of this type of analysis is that once an ion's mass has been determined as a unique compound, that known measurement can then be used to determine the same analyte's mass in a mixture, as long as .respectively, and ρw is the density of water (1000 kg/m 3). This method for determining soil moisture is referred to as the gravimetric method. In the field moisture content can be measured in a number of other ways. Electrical resistance blocks use the inverse relationship between water content and the electrical resistance of a
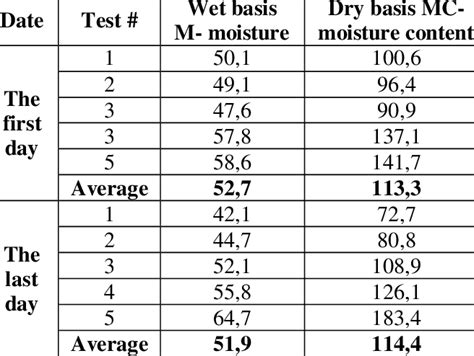
There are many ways to measure soil moisture, though the gravimetric method of soil moisture measurement is the most accurate, however, it is not suitable for real-time or large-scale field studies due to labor- and time-intensive procedures. In other words, the gravimetric method-based soil moisture measurements are not very feasible for . Gravimetric Soil Moisture Detection. This method extracts water from a soil sample through evaporation, flushing, and a chemical reaction. The gravimetric soil moisture is calculated based on measuring the difference between the wet and dry sample weight. GWC (%) = [(mass of moist soil (g) − mass of dry soil (g)) / mass of dry soil (g)] × 100This direct technique is usually referred to as the thermo-gravimetric method (or simply gravimetric) when expressing water content as weight of water over weight of dry soil, GWC[lb 3 lb-3] (i.e., the ratio of the mass of water present in a sample to the mass of the soil sample after it has been oven-dried (100–110 °C) to a constant weight). Comment to gravimetric method. 1. Soil-water content changes over time, and with depth and in space. Changes in soil-water content are usually at a maximum at the soil surface and in the upper soil layer. Soil samples have to be large enough to be representative, but not too big as to lose information about the distribution of soil-water .
The difference in the gravimetric test is whether the gravimetric soil moisture content (θg) is done iteratively [10], . The sensor is an indirect method of soil moisture measurement. The .
WEBVeja a programação da semana e compre seus ingressos direto no site da Moviecom
gravimetric method in soil moisture|soil moisture content chart